We are starting a new monthly series delving into the MIDDLE MANAGER. First up, let’s explore the top concerns that have the most negative effect on a middle manager’s experience, which may vary based on individuals and work environments. These challenges stem from various sources, including top-down directives, organizational bureaucracy, outdated structures, and lack of effective communication.
Here’s a breakdown of the most common concerns:
- Lack of Trust and Autonomy:
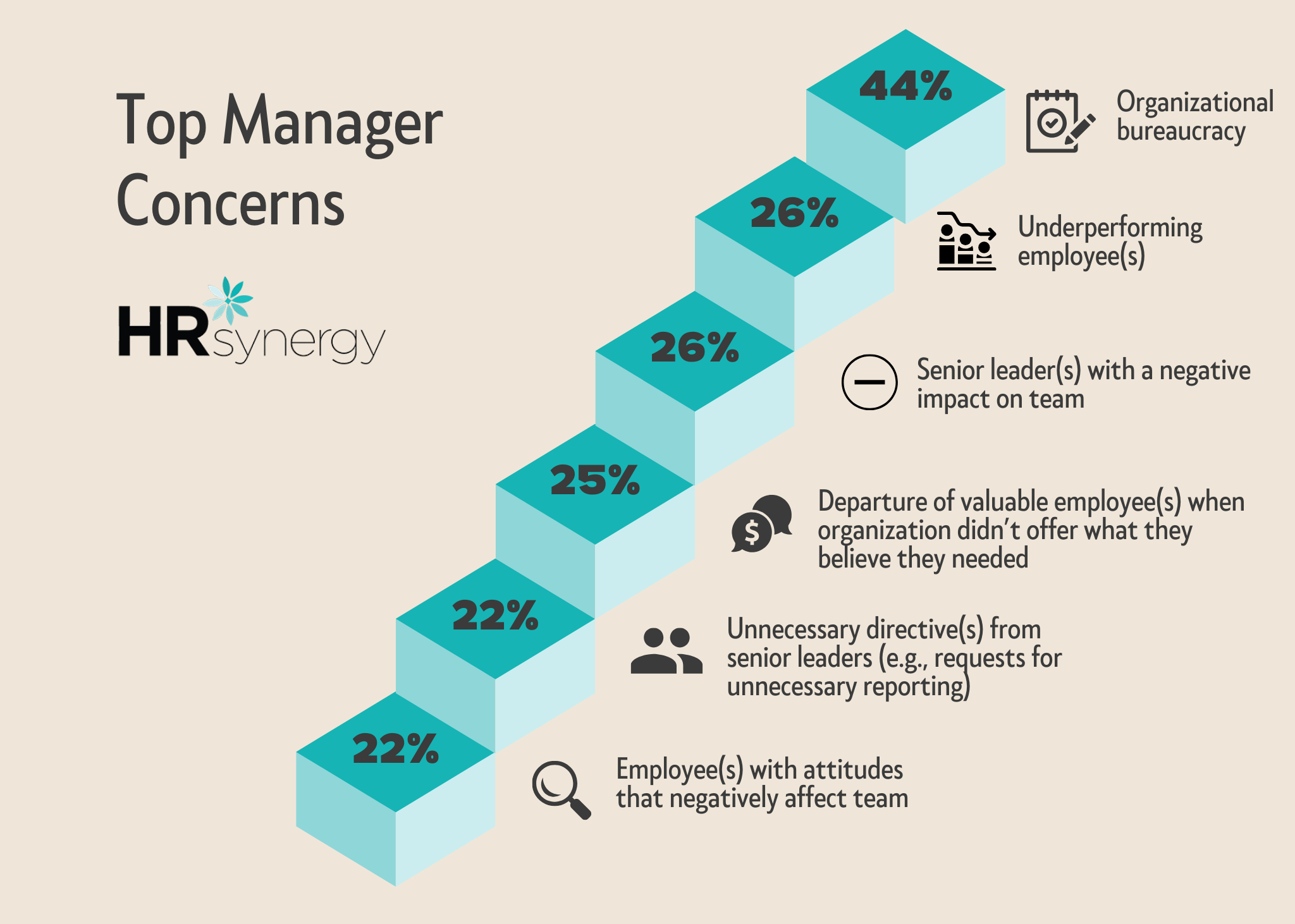
Middle managers desire increased autonomy and trust from top management. Lack of decision-making authority can make it difficult for managers to lead effectively. Middle managers often spend a significant amount of their time on administrative tasks and bureaucratic processes, which tend to be redundant or unnecessary. When they are burdened with excessive administrative tasks and micromanagement, they feel undervalued and constrained in their ability to make meaningful contributions and strategic decisions, hindering their effectiveness in leading the team and achieving organizational goals efficiently.
- Team dynamics:
Managing underperforming employees can be challenging and time-consuming, affecting team productivity and the cohesion of the team.
Negative attitudes within the team can create a hostile work environment, disrupt teamwork, and hinder the manager’s efforts to maintain a positive and productive atmosphere.
Negative senior leaders can create a toxic work environment, diminish employee morale, and reduce the manager’s ability to lead effectively.
Therefore, underperforming team members and negative employees and senior leaders can cause the departure of your valuable employees. Losing valuable employees due to unmet needs can disrupt team dynamics and affect overall productivity. Also their quitting creates additional workload for managers who must handle the gaps left by departed employees.
- Work-life balance:
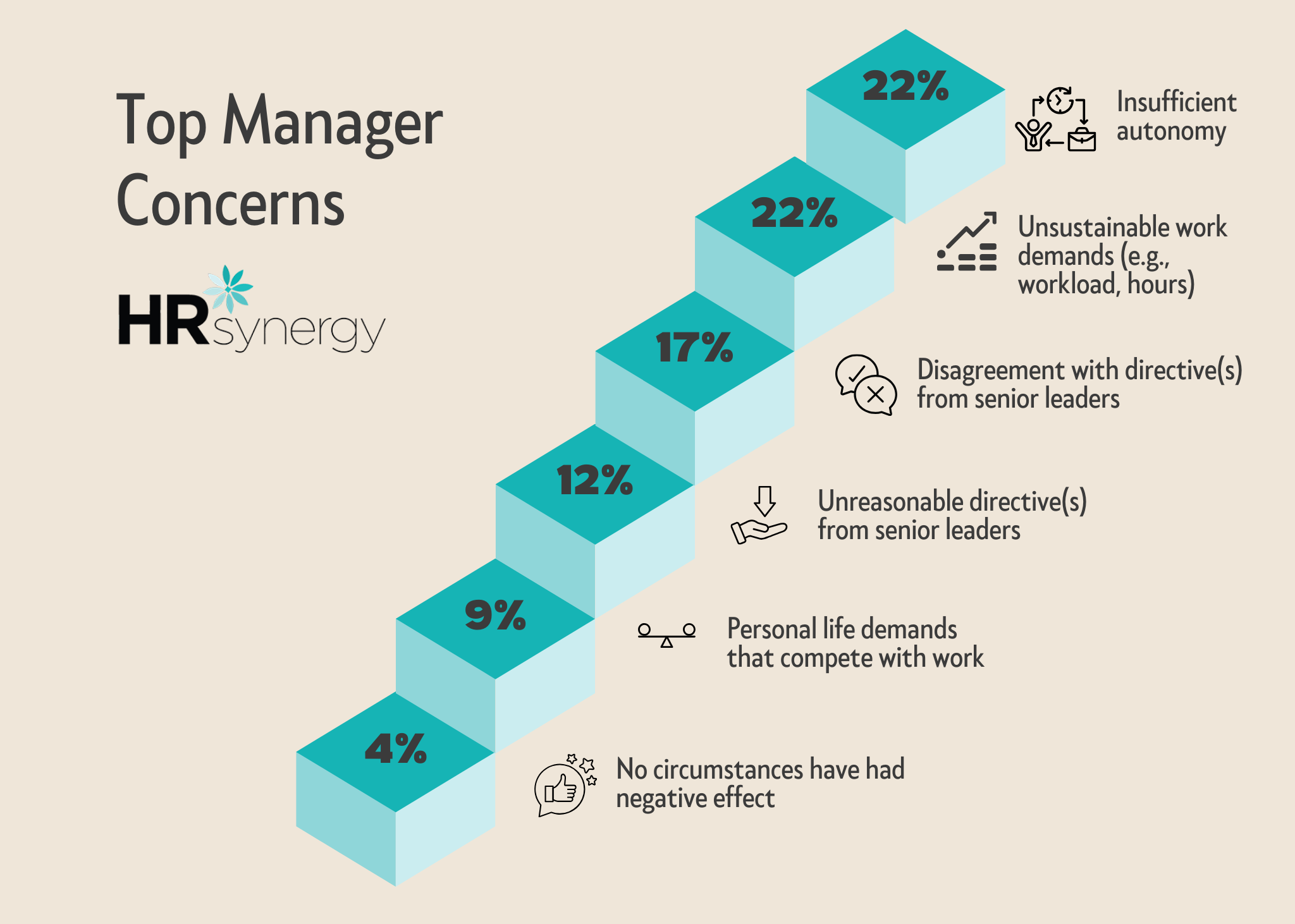
Personal life demands that compete with work responsibilities can also be difficult for managers, impacting their overall well-being and work-life balance. Excessive workload, long hours, and unrealistic expectations can lead to burnout, stress, and a decline in the overall well-being of managers.
- Communication Gap:
Middle managers often find themselves caught between the directives from top leadership and the need to motivate and guide their teams. The lack of clear communication and understanding between top management and middle managers creates confusion and inefficiencies.
Unnecessary directives, unreasonable directives, and those the middle manager disagrees with put immense pressure on middle managers. This leads to frustration for managers and hinders their ability to focus on strategic tasks. Conflicting directives can create confusion and make it challenging for managers to align their team with the organization’s goals. Ultimately, frustrations with directives can make it difficult to efficiently meet expectations and maintain team motivation.
Here are other impactful concerns for middle managers:
Outdated Structures:
Many companies have not adapted their organizational structures to keep pace with technological advancements. Outdated structures limit the effectiveness of middle managers and hinder their ability to lead in a rapidly changing business landscape. Resistance to change and reluctance to invest in restructuring can perpetuate the existing problems.
Importance of Feedback and Solutions:
Executives need to actively seek feedback from middle managers and involve them in decision-making processes. Middle managers are uniquely positioned to offer insights and solutions to the challenges they face, making their input invaluable for creating effective strategies for improvement.
Negative Stereotypes:
Popular culture and some executives perpetuate negative stereotypes about middle managers, undermining their confidence and effectiveness. This perception can lead to middle managers being undervalued and potentially removed from their positions.
Each of these concerns highlights specific challenges that managers may face within their organizations. Addressing these concerns through supportive organizational policies, effective leadership training, and fostering a positive workplace culture can significantly improve a manager’s experience, maintain a positive work environment, and enhance their ability to lead effectively.
Sign up for our MIDDLE MANAGERS TRAINING! 4th Thursday of the month. Upcoming trainings June 27, July 25 3-4pm.
Read more from our MIDDLE MANAGERS SERIES:
The challenges faced by middle managers
Some key managers’ desires and potential solutions
1st-time managers often are ill-prepared for their new role
Caring for Caregivers: A Manager’s Guide to Supporting Employees in Their Caregiving Roles
Tips for New Managers Who Are Now Supervising Their Former Peers
Managing Difficult Employees and Disruptive Behaviors: A Comprehensive Guide for HR Professionals
Empowering the Middle: How HR Can Support Middle Managers in a Hybrid Workplace